CS61CPU
Look ma, I made a CPU! Here’s what I did:
I mainly follows the cs61c-sp22’s course. And this project gives me lot’s of sense of fulfillment.
1 Architecture
These are the mainly works need to be implemented in this project.
2 Study Experience
Thanks a lot to cs61c’s teacher group. Intuitive suggestions are given in this project instructions. And here are some difficulties I met in this project.
-
Control logics. This can be implemented by ROM or HardWare. And I use ROM to realize the control logics, which can tell selection bits according to instruction name. So some comparators and constant values are used to match Opcode, funct3 and funct7 to get the instruction. And then for the first 32 instructions excluding jalr, jal, auipc and lui, I use a priority encode to map them to 0-31. And for the excluded 4 instructions, I mapped them to 0-3 and added it to 32. The map method is not so important, but the thoughts to use priority encoder is important.
-
Two level pipeline. I was stuck here at first because I didn’t make myself understood how pipeline works in lab6. This project requires to realize a 2-stage pipeline, and one is instruction fetch, the other is execution. And control hazards may occur. Here is a simple question, that is why there is no data conflicts or structural conflicts. The answer is that we only have 2-stage, and instruction fetch won’t affect the execution, it doesn’t try to read from or write to a register. But in the execution stage, we may want to use pc, whether branch instruction use pc or jump instructions use pc+4 to set rd. But when we execute, the pc is different. So except the instruction register, we also need a pc register, to store the current execute program counter. And two questions asked in the project manul is,
To MUX a no-op into stage 2, do you place it before or after the instruction register?
Answer: So, first, why we need no-op. Because control hazard may occure in this model. And candidate instruction loaded may be not what we want. So we replace it by a no-op instruction. Second, how do we know there is a control hazards. When the pc sel is true, it will jump to some other instruction, instead of the pc+4 instruction. Third, when should we do the choice. Before the next instruction loaded or after next instruction loaded. The answer is before the candidate instruction loaded. I think there is two benefits. First the mux needs time to execute, when we set it before, the cpu will run faster. And for another reason, if we set it after the instruction register, the last instruction has been executed, the pc sel is not valid.(Here I am not sure)
What address should be requested next while the EX stage executes a no-op? Is this different than normal?
Answer: It’s as normal. When we execute no-op, it means there is a branch or jump. So the pc is already setted. And this side proves why we need this no-op. It need to remove the pc+4 already loaded. After no-op executes, the instruction at jump address will be loaded from Instruction Memory.
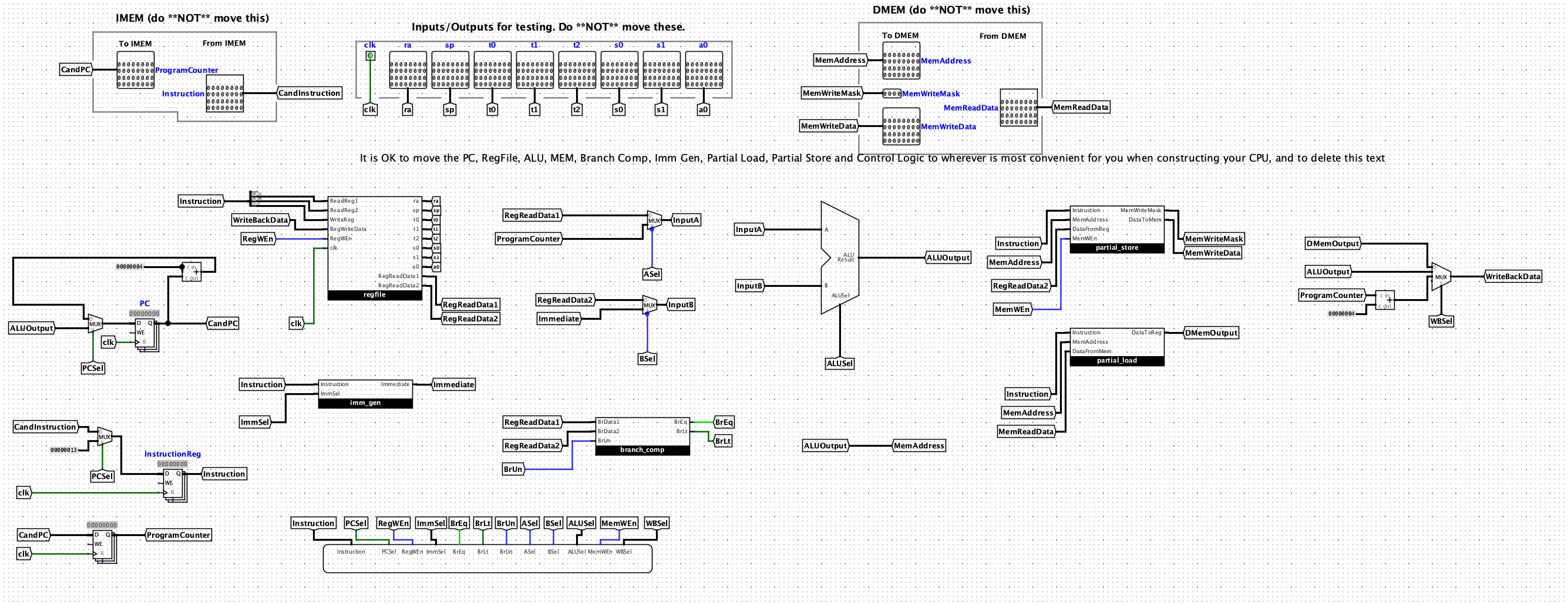
Here is the logic circuit I made. So amazing.