This is a review of reading delaunay code’s problem.
1 Pipeline
This pipeline is set simply on some nodes file. Many details are omitted.
- Read nodes file, make nodes’ which has (x,y,z) coordinate as input.
-
Sort vertices. (So for here I don’t know much, I may igorned some details). Then do some initialization.
- Then insert them one by one into the triangle. And here comes the flip operations, you can see these operations below in the flip operation.
2 Example
Below is a simple example, that maybe helpful to understand the whole pipeline.
2.1 Conditions
-
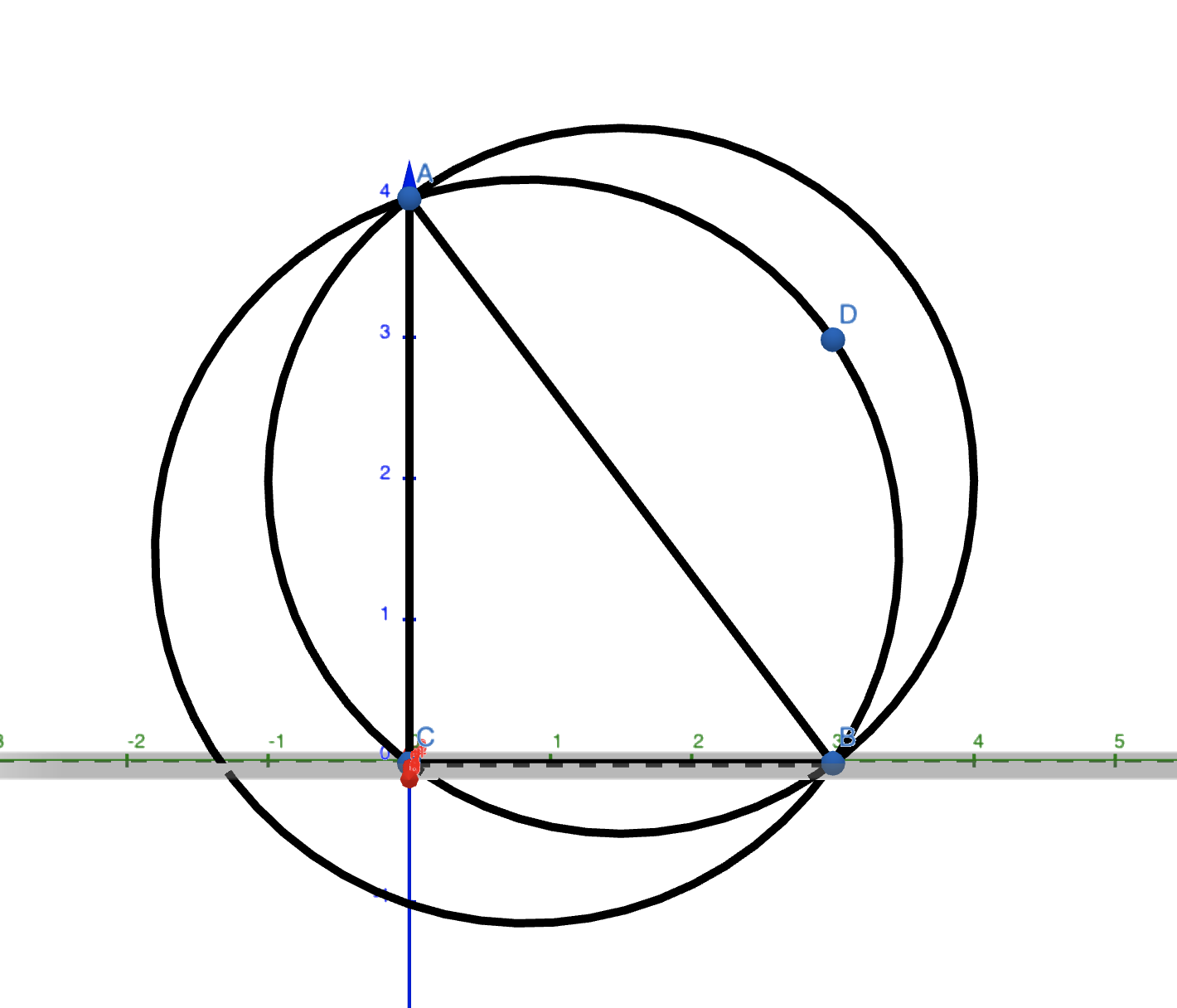
Considering this, we have only 4 only points. So in this example, we will have 5 points including the infinite vertex. A(1,4), B(4,0), C(1,0), D(4,3) . And we made the inf_vert as (0,0).
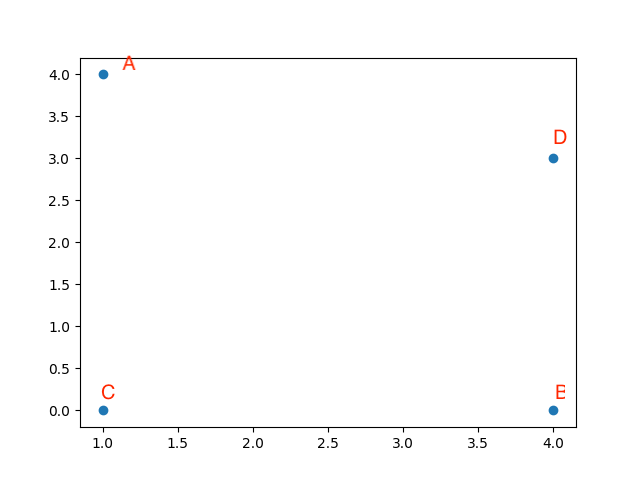
-
As we want to test the lawson flip, we need to construct the condition first. The program will automatically sort the vertices. So we manually construct the triangle below.
2.2 Process
-
Construct the first triangle. The first triangle is (A,B,C)
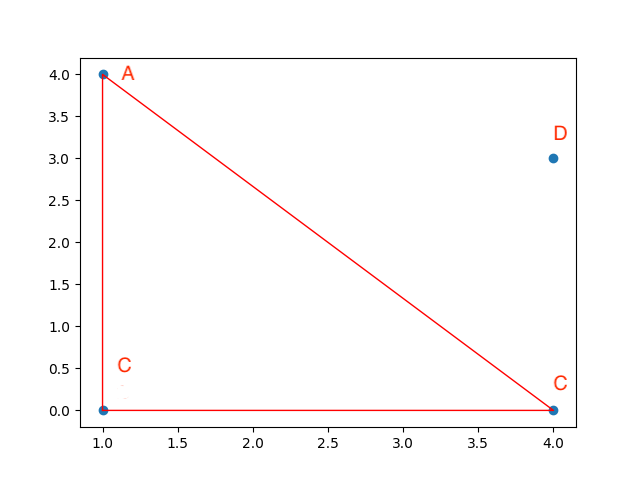
-
Here when we insert D(4,3), we need to do flip13. The function of flip13 you can see in the 3.1.
And we are gonna to explain flip13 in detail.
So first we get 3 vertices of the first triangle.
Vertex *pa = tt[0].org(); // pa(1,4) Vertex *pb = tt[0].dest(); // pb(4,0) Vertex *pc = tt[0].apex(); // pc(1,0)And then we use a for loop to travel through the half-edges of this triangle and get all the neighbor halfedges.
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++) { nn[i] = tt[0].esym(); // nn[0] = B->A, nn[1] = C->B, nn[2] = A->C tt[0].ver = _enext_tbl[tt[0].ver]; }Construct three edges, tt[0] (A,B,D), tt[1] (B,C,D), tt[2] (C,A,D). This operation can be understood when the vert is in triangle. But it’s may be hard when it’s outside the triangle.
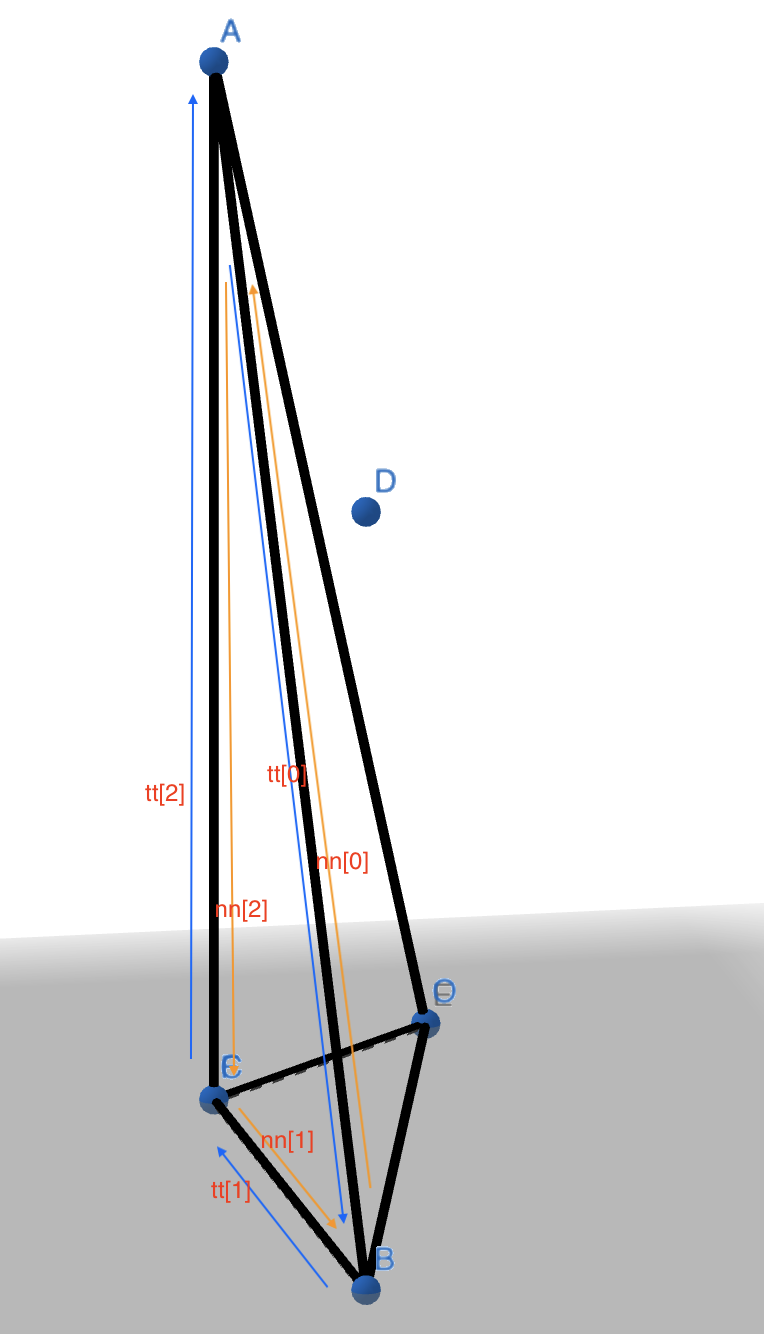
And we use the origin to nn to connect the newly created triangles. Meanwhile, we need to set boundary, exterior and some other parameters which I didn’t pay much attention to it now.
After we create 3 new triangle(maybe), we will step into the next stage. There are some edges to flip. We need to collect them and have a check.
Collect. In flip13, first we need to collect the tt[i], that is A->B, B->C, C->A these 3 edges. After this, we need to collect the paired half-edges. The code is below. From my opinion, it’s just travel around all the triangle which is adj to triangle A,B,C. And finally return back.
do { N.set_edge_infect(); * (TriEdge *) fqueue->alloc() = N; N = N.eprev_esym(); } while (N.tri != (*ppt)->adj.tri);You can see 3 other edges are pushed into the fqueue, which are to flipped.
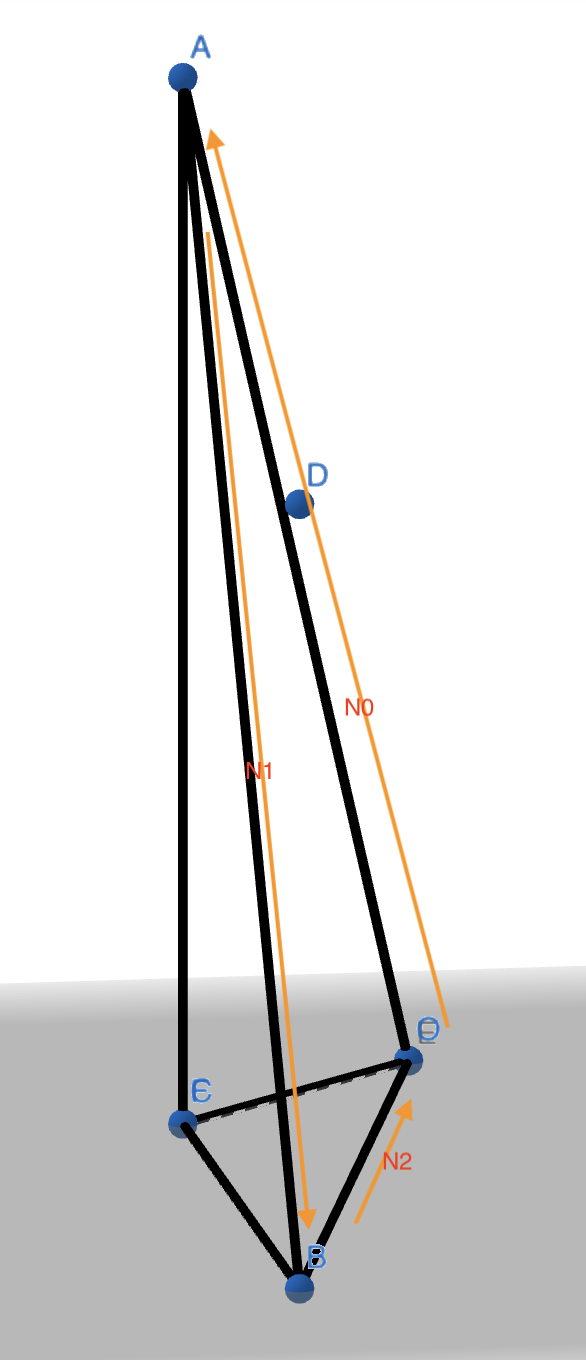
-
And we come to the key stage. Current triangulation is not deluanay triangle. We need lawson flip to check it.
In lawson flip, we need to check the edges which may need flip operations.
ori = false; ishullflip = 0; tt[0] = *pte; // a->b->d tt[1] = tt[0].esym(); // c->b->a // both of them or not hull triangle if (!tt[0].tri->is_hulltri()) { if (!tt[1].tri->is_hulltri()) { // An interior edge. if (op_db_verbose > 3) { printf(" O3d: (%d, %d, %d, %d)\n", tt[0].org()->idx, tt[0].dest()->idx, tt[0].apex()->idx, tt[1].apex()->idx); } ori = regular_test(tt[0].org(), tt[0].dest(), tt[0].apex(), tt[1].apex()); } }(这里有不理解,这里传进去的是A,B,D,C,而Orient3D的意思是如果C在ABD平面下方则为正数返回)
-
“When the ori get from the step 3 is generated, and ori>0, then the edge is locally non-regular and non-convex.” (这里的non-regular 以及 non-convex是什么意思。) So we need to use flip_check to check how to flip this edge. And we get AB intersects with CD, so we need to use flip22 to delete AB.
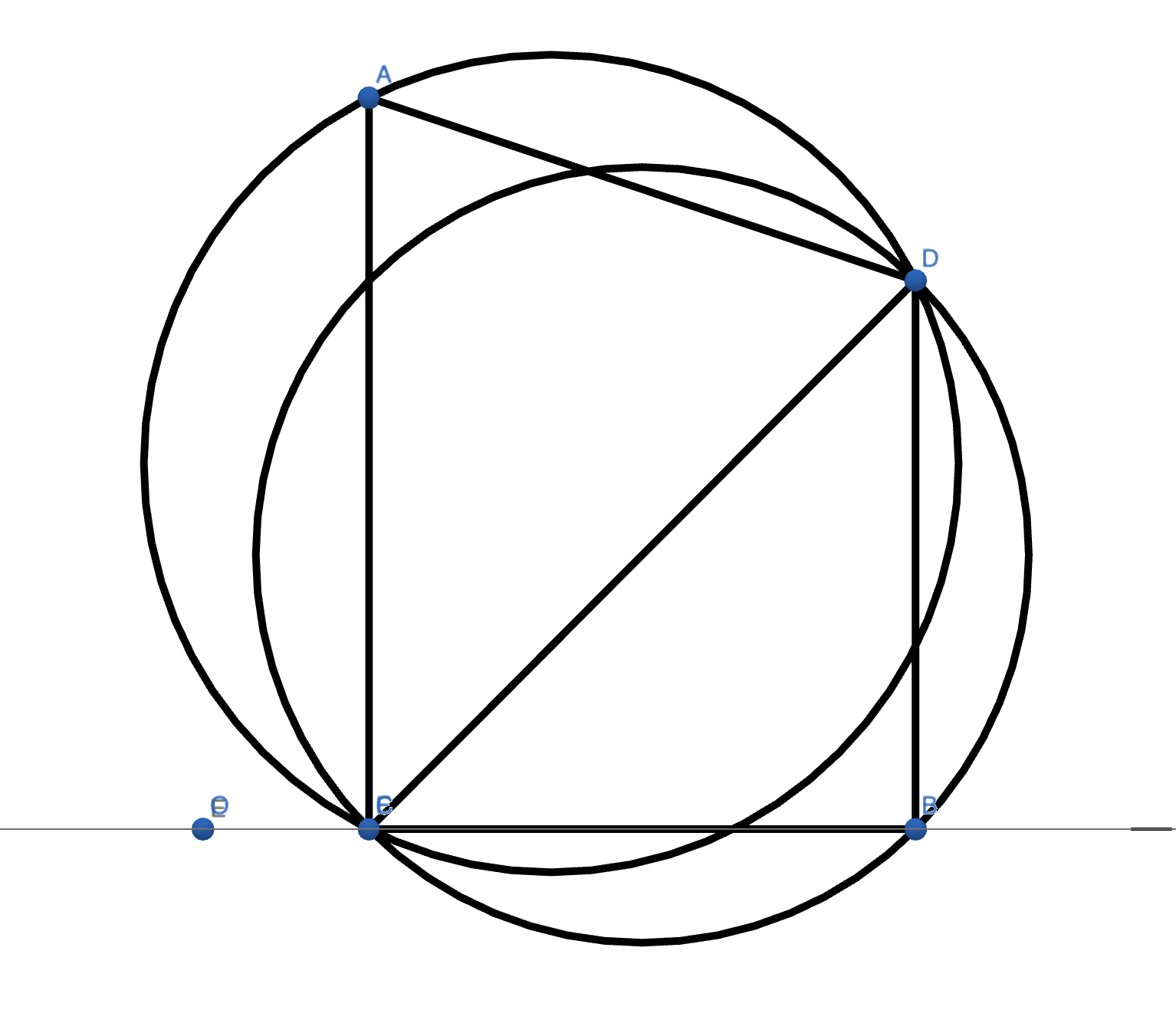
In flip22, the main operation is to build two new triangle, which is (c,d,b) and (d,c,a). The result is shown below in the picture. And rebuild the connection. After flip22, we can get some edges to flip, so we still go to lawson flip until all the edges needing flip are emptied.
3 Flip Operation
FLIP
- Do FLIP operation according to the vertex pos. We have flip13, flip22, flip24, flip42 and so on.
- Then we need to get the vertices which are infected. And then push the infected edges into it. For FLIP13 and FLIP24, we not only add the origin triangle edge also the newly created 3 edges.
3.1 FLIP13
This situation happen’s when the vertex to be inserted is in triangle or outside the triangle.
-
Find the neighbors of triangle which the edge is on.
-
Counstruct new 3 triangles.
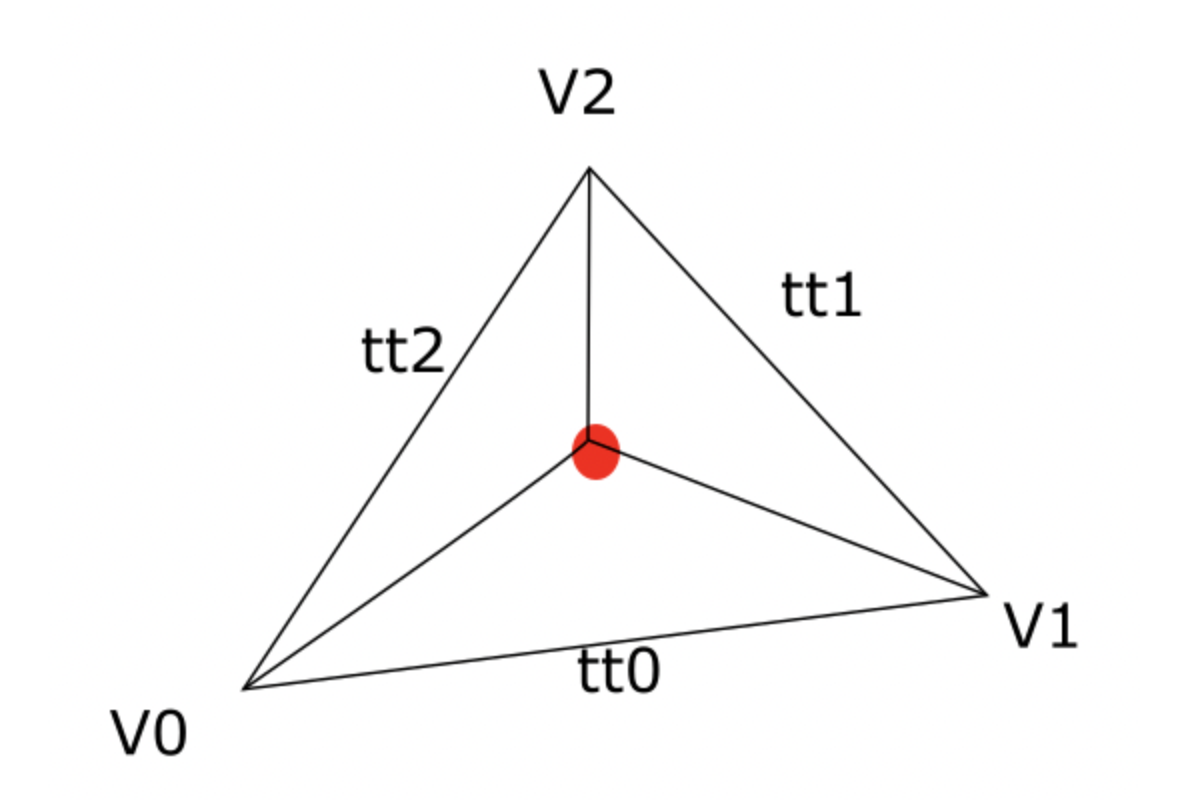
-
Connect the newly constructed triangles with the neighbors found previously.
-
After that, set the hull tag? I don’t know much about it.
3.2 FLIP24
This situation happen’s when the vertex is on one edge. I made a special
3.3 FLIP 42
3.4 FLIP 22
3.5 Lawson Flip
Lawson flip is to make some cases which is not a Delaunay triangulation to a Delaunay triangulation.
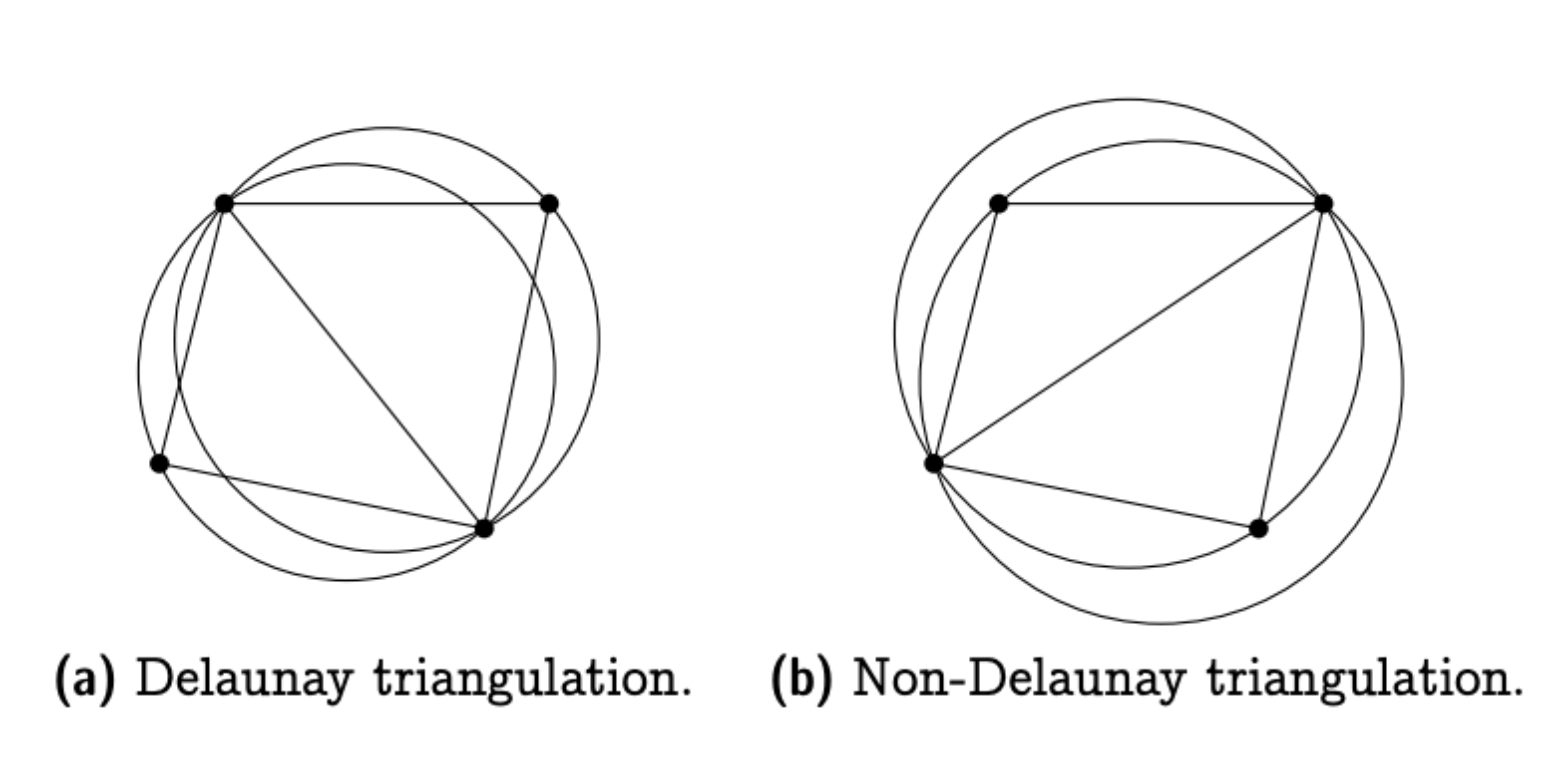
Below picture refers from ti.inf.ethz.ch/ew/CG13/lecture. So what the lawson’s flip do in the below picture is to turn (b) to (a) in order to satisfy the constraints of Delaunay triangulation.
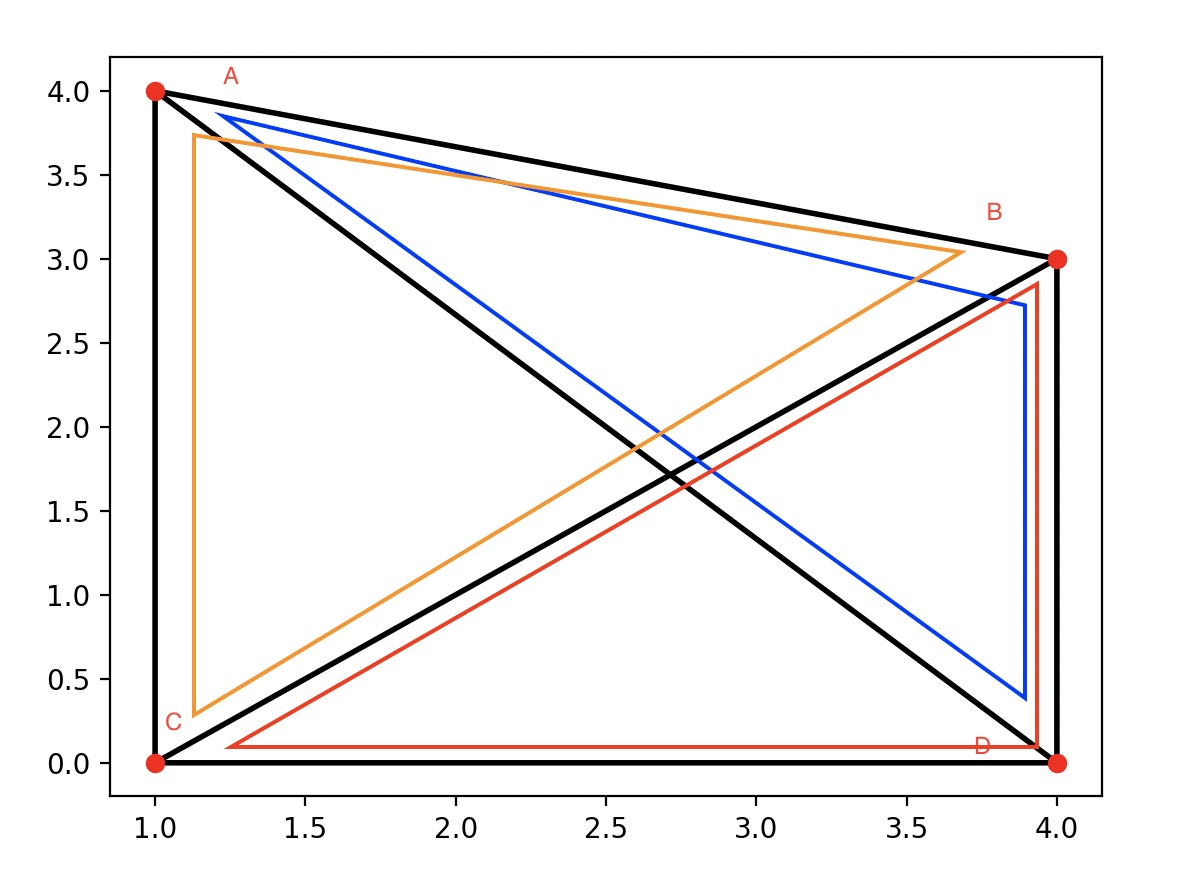
I used a special case to test lawson flip. Below is the case, we have 4 coordinates, which is \(a(0,0), b(3,0), c(0,4),d(3,3)\) As the algorithm random permute the vertices at the beginning, I made the first triangle manually which is (a,b,c). And now what we need to do is to insert d(3,3). Below is the situation.
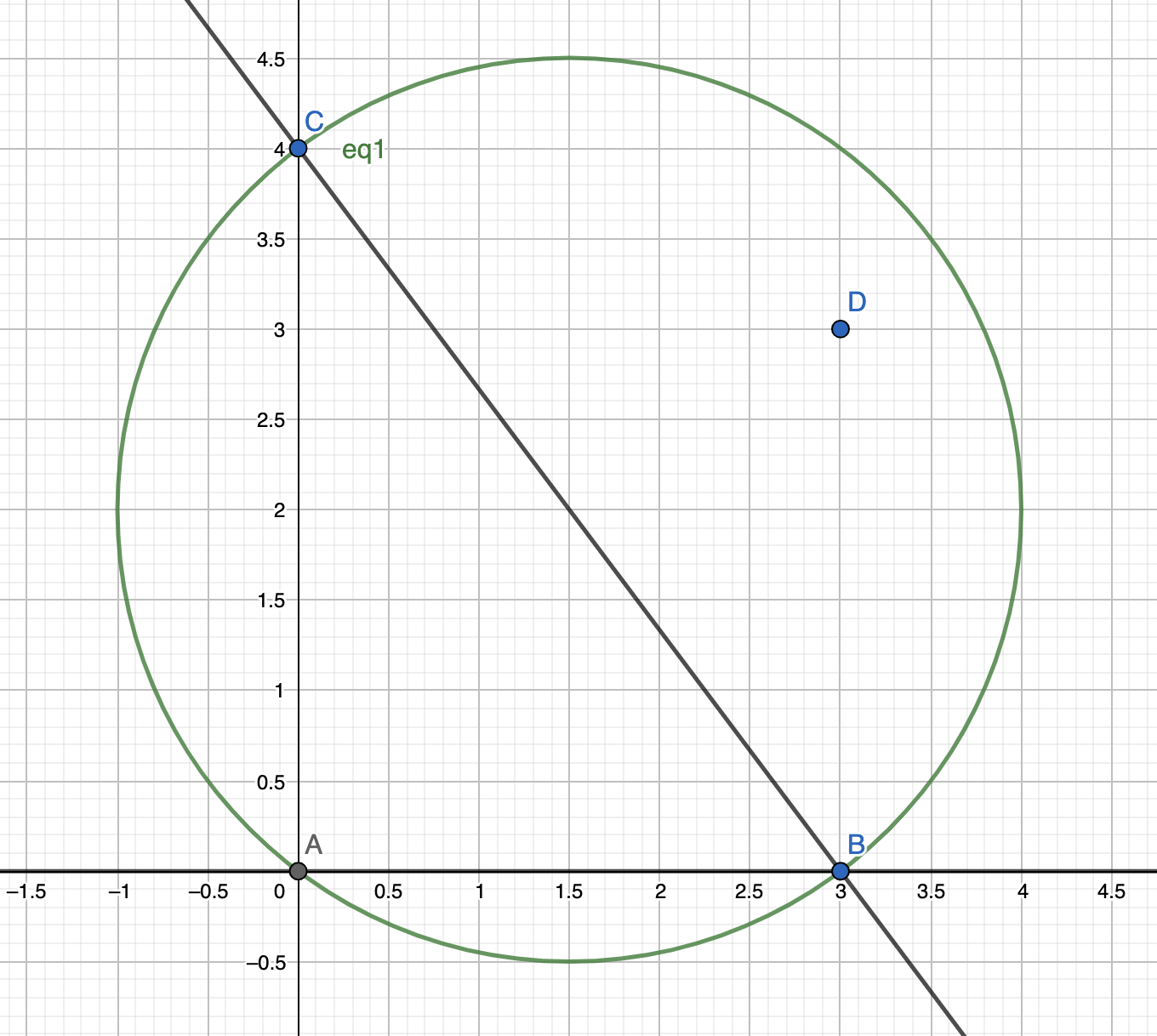
So, after we insert the d(3.0,3.0) into the plane. We will note d is in the external circle of triangle(a,b,c).
Detri2
- What’s the segment here ?
- a inf vertex
- what is hull triangle
process is below
initialize(){
// init vertex and segment
// a infvertex
initialize_lookup_table(); // init the bitmasks
reset_options();
}
Triangulation tr = new Triangulation();
tr->parse_commands(argc,argv);
tr->read_mesh();
tr->reconstruct_mesh(0);
排序之后开始插点,如果三角形为空,就从里面拿3个出来。之后还需要新建三个假的邻接三角形。接下来开始插点,插点首先要确定点的位置。进入locate_point,根据点位返回不同的结果,有在三角形里,在边上,在点上有点不理解。得到如果为逆时针,就变成顺时针。做flip操作,每一种情况都有对应的lawson flip。flip之后进行lawson flip。lawson flip实际上是说,需要递归的去翻转点边。
void exactinit(int verbose, int noexact, int o3dfilter, int ispfilter, REAL maxx, REAL maxy, REAL maxz)
int Triangulation::sort_vertices(Vertex* vrtarray, int arysize, Vertex**& permutarray)
void brio_multiscale_sort2(permutarray, arysize, so_brio_threshold,
so_brio_ratio, so_hilbert_order, so_hilbert_limit,
io_xmin, io_xmax, io_ymin, io_ymax);
重要的类
class Triangulation{
public:
arraypool* tr_steiners; // Stenier vertices 狭窄的顶点???
arraypool* tr_segs;
arraypool* tr_tris; // exm这又是啥
}
-
Locate_point 三角形
当没有三角形时从0构建1个。并且确定是顺时针还是逆时针。里面判断hull triangle。
-
Flip13 遍历三角形的所有边,拿到邻接的所有三角形。
笔记
- Orient2D是一个线性规划,解一个不等式
- 使用exactinit的原因可以在 triangle_exact
- 这些名词解释很有用definition
问题
- 在初始化Triangulation时,初始化了一个tr_infvrt,这个tr_infvrt是什么。
- 在放点的时候,要找到一个说组成的三角形位置是逆时针的,但这个edge为什么可以表示为3个点。
- locate_point没看懂。看懂了,是个线性规划。
- 为什么需要维护一个内存池子,懂了因为这个池子里是需要翻转的边。
- Delaunay 45 行,
- 这个locate point是不是有点类似于正弦定理,乘出来小于0就怎样,大于0就怎样。如果这个点在三角形里,他需要满足和其中的两个三角形为逆时针。
- 为什么需要 _vo , _vd, _va这三个数组。
- TriEdge里的 apex(), org(), dest() 的原型是什么,org->origin, dest->destination,可是为什么是个函数。
-
PSLG的定义还不太理解“Segments are edges whose endpoints are vertices in the PSLG, and whose presence in any mesh generated from the PSLG is enforced.” 以及CCDT,CDT
- is_hulltriangle()
- what’s flip ?
- Set_edge_infected 一个位操作
- hull flag
- what’s boundary marker?
- Flips 924 exposed edges.
- lawson’s flip Delaunay 265 ? locally regular?
- When will flip42 and flip22 be used.
- lawson flip’
- Sort_vertices.